
Nearly two years after releasing its first Ryzen 5000 desktop processors, AMD is finally ready to follow them up. Today, the company announced pricing and availability for the first wave of Ryzen 7000 CPUs based on the Zen 4 architecture, along with more details about the accompanying AM5 platform and the performance increases that early adopters can expect.
The first four Ryzen 7000 CPUs will be available on September 27, and AMD is using the same strategy it used to launch the 5000 series (if you're wondering about the skipped number, 6000-series CPUs are only available for laptops). It's starting with four higher-end, higher-priced parts, while lower-end CPUs for mainstream and budget builds will follow next year.
| CPU | MSRP | Cores/threads | Clocks (Base/Boost) | Total cache (L2+L3) | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 7600X | $299 | 6c/12t | 4.7/5.3 GHz | 38MB (6+32) | 105 W |
| Ryzen 7 7700X | $399 | 8c/16t | 4.5/5.4 GHz | 40MB (8+32) | 105 W |
| Ryzen 9 7900X | $549 | 12c/24t | 4.7/5.6 GHz | 76MB (12+64) | 170 W |
| Ryzen 9 7950X | $699 | 16c/32t | 4.5/5.7 GHz | 80MB (16+64) | 170 W |
AMD is sticking to the same core counts it used for Zen 3. The entry-level model is the 6-core Ryzen 5 7600X, launching for the same $299 that the 5600X cost in 2020; the 12-core Ryzen 9 7900X is also launching for $549, the same price as the Ryzen 9 5900X. The other two chips are a little cheaper than their Ryzen 5000 counterparts; the 16-core Ryzen 9 7950X launches for $699, $100 less than the 5950X, while the 8-core Ryzen 7 7700X starts at $399, $50 less than the launch price for the Ryzen 7 5800X (technically, this is a price increase over the $299 Ryzen 7 5700X, but that chip wasn't released until nearly a year and a half after the 5800X).
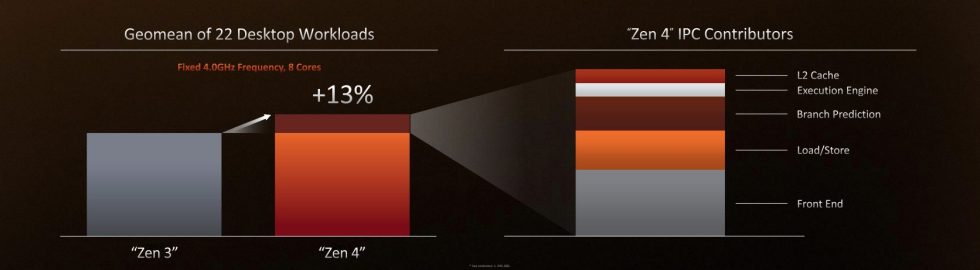
AMD says that "optimizations" made over the course of Zen 4's development have increased its instructions-per-clock (IPC) increase over Zen 3 to an average of 13 percent, up from the 8–10 percent increase the company promised earlier this year. The maximum clock speed of the 7950X has already increased to 5.7 GHz, 800 MHz faster than the boost clock of the Ryzen 5950X. All told, this should make the 7950X an average of 29 percent faster than the 5950X at tasks that benefit from single-threaded performance, including games.
During its launch event and during a Q&A session for media and analysts afterward, AMD hesitated to get too far into the weeds about Zen 4's architecture and pointedly stayed away from projections about when we could expect other Zen 4 chips to launch. But you shouldn't expect 3D V-Cache versions of Zen 4 or lower-end, lower-cost Zen 4 CPUs until sometime in 2023.
Performance and power efficiency gains
We'll learn more about the changes to Zen 4's architecture between now and when the CPUs launch, but the company shared a few details about where the performance and power efficiency improvements are coming from.
AMD Chief Technical Officer Mark Papermaster says that Zen 4 is a revision of the Zen 3 architecture that focuses mostly on the "front end" of the architecture to more efficiently fetch and pass tasks along to the improved execution engine that was the focus of Zen 3. (Papermaster also says that Zen 5 will be a more substantial "ground up" redesign, but we don't expect to hear many details before 2023 or 2024). Most of Zen 4's 13 percent IPC boost comes from these optimizations, while branch prediction, a doubled L2 cache, load/store improvements, and further small execution engine tweaks account for the rest.
Specific tasks like machine learning and AI workloads can also benefit from the introduction of AVX-512 extensions. This puts Intel in a strange spot—the company defined these extensions nearly a decade ago and was alone in pushing them for years. But it has disabled AVX-512 support in its 12th-generation CPUs because the processors' efficiency cores don't support it. These extensions have been a bit controversial because using them can consume a lot of power and because the workloads that benefit from them are specialized and relatively rare (Linux creator Linus Torvalds has said that he hopes "AVX-512 dies a painful death"). But it is a bit funny that AMD's latest CPUs will now support them while Intel, the company that invented them and pushed to popularize them, sells CPUs that cannot.
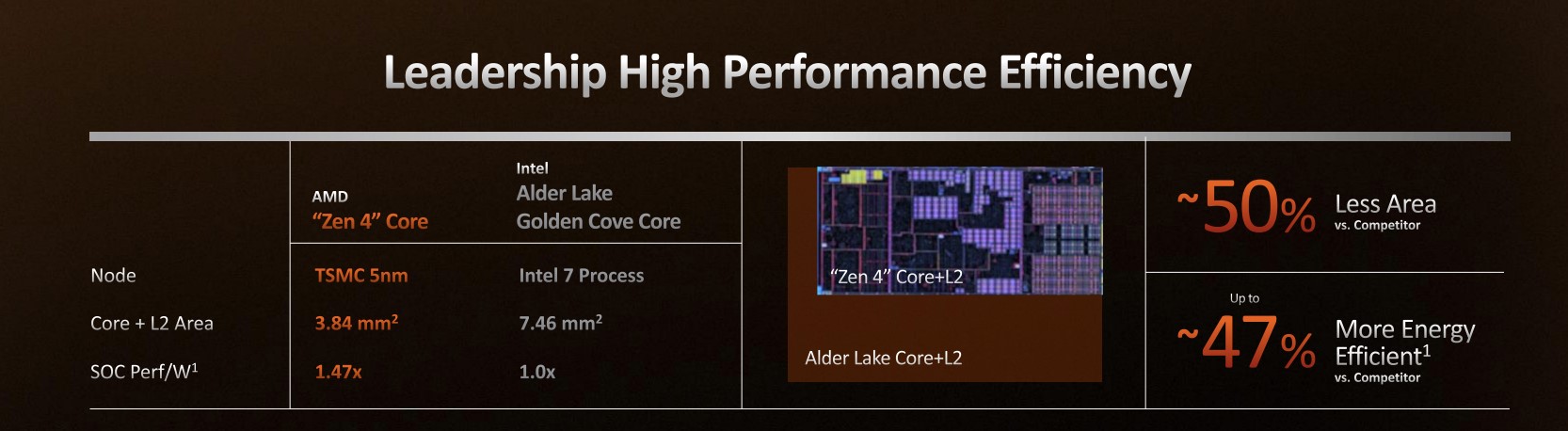 A better manufacturing process (among other things) makes a Zen 4 core much smaller than an Intel Golden Cove core (this is the P-core architecture for the current 12th-gen Alder Lake CPUs and the upcoming 13th-gen Raptor Lake).AMD
A better manufacturing process (among other things) makes a Zen 4 core much smaller than an Intel Golden Cove core (this is the P-core architecture for the current 12th-gen Alder Lake CPUs and the upcoming 13th-gen Raptor Lake).AMD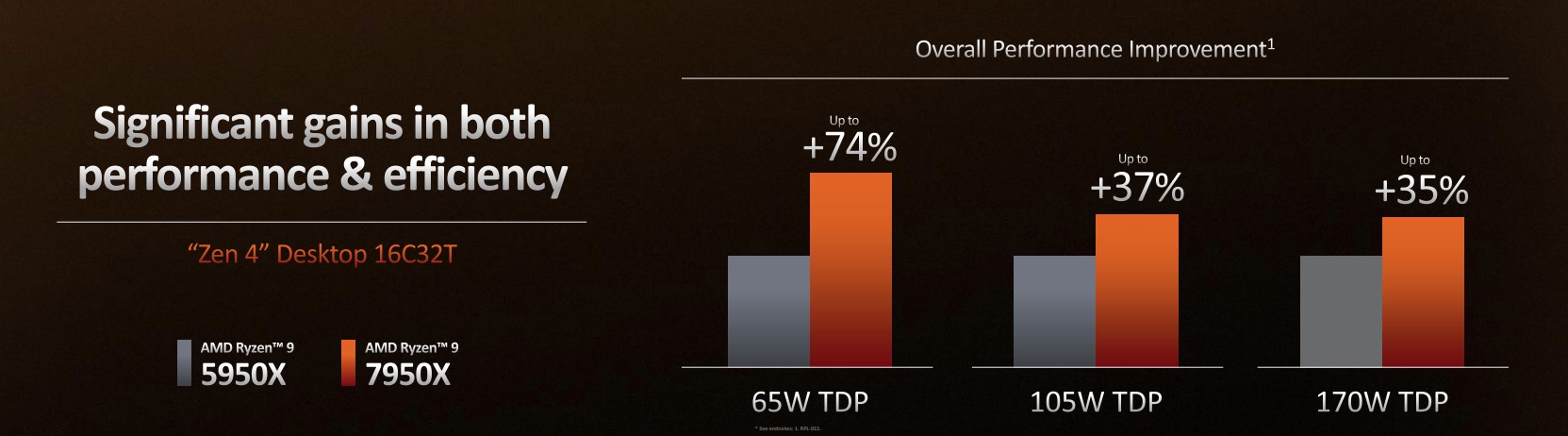 AMD's power efficiency improvements over Zen 3 are also notable, especially at lower TDPs. No 65W TDP chips are being launched today, but they should follow, given time.AMD
AMD's power efficiency improvements over Zen 3 are also notable, especially at lower TDPs. No 65W TDP chips are being launched today, but they should follow, given time.AMD
Even with AVX-512 support added, AMD says that a Zen 4 core and its accompanying L2 cache takes up 50 percent less area than one of Intel's current-generation P-cores (though this is at least partly because you're comparing TSMC's 5nm manufacturing process to the older Intel 7 process, and partly because a Golden Cove core has 1.25MB of L2 cache while a Zen 4 core has a flat 1MB). AMD also says a Zen 4 core is "up to 47 percent more energy-efficient" than a Golden Cove core.
AMD also makes big claims when comparing Zen 4 to the previous-generation Zen 3, especially around performance-per-watt. Comparing the Ryzen 9 7950X to the Ryzen 9 5950X at the same TDP levels, AMD says Zen 4 should outperform Zen 3 by about 35 percent when set to a 170W TDP, by about 37 percent when set to a 105W TDP, and by a whopping 74 percent when set to a 65W TDP.
This kind of efficiency improvement is important, because the CPUs that ship in pre-built OEM systems often use these lower stock TDP levels rather than the boosted TDP levels that are possible with custom-built systems and more full-featured motherboards. More efficiency is also handy for mini-ITX systems, where you might not have the cooling capacity to let the CPU consume tons of power and generate tons of heat.
AM5 will be supported until at least 2025 (and other platform details)

Thanks to a steady drip of official announcements and leaks, most of the high-level facts about the AM5 socket and the 600-series chipsets will be familiar to those who have been paying close attention. All Ryzen 7000 CPUs and motherboards will require DDR5 RAM, with no backward compatibility for DDR4; AM5 is a 1718-pin LGA socket that puts its contact pins on the motherboard rather than the bottom of the CPU; AM5 can deliver as much as 230 W to processors with a maximum TDP of 170 W, and the socket will remain compatible with all of the AM4-compatible CPU coolers already out there.
But we did get a few new tidbits. One is that AMD is committing to supporting the AM5 processor socket until at least 2025. This may not sound like a lot when you compare it to the five-plus-year life cycle of the AM4 socket, but AMD's support of AM4 has also been a little bumpy—older AM4 motherboards and chipsets weren't going to be allowed to use Ryzen 5000-series CPUs at all. It could be that AM5 is supported for longer, and AMD wants to set lower expectations so that people don't get as upset when new CPUs don't work in 5-year-old motherboards. The only way to know is to wait and see.

AMD is also pushing its automatic memory overclocking feature, dubbed EXPO (or EXtended Profiles for Overclocking). EXPO-tested DDR5 memory kits will be able to run at speeds of up to DDR5-6400 at launch, and AMD also says that it will continue to support auto-overclocking for RAM that uses Intel's Extreme Memory Profile (XMP) instead. I would be astonished if most DDR5 RAM kits don't end up advertising both, given that they are different names very similar things.

We also learned about one new chipset that we hadn't heard anything about before, the B650 Extreme. Like the X670 Extreme, B650 Extreme motherboards will provide PCi Express 5.0 lanes to both the M.2 SSD slot and the GPU slot, while non-extreme X670 and B650 motherboards will have PCIe 5.0 SSD support but stick to PCIe 4.0 for GPUs. AMD says that all chipsets will support the same level of CPU performance at stock settings and will retain overclocking capabilities (though based on past precedent, it's probably safe to say that X670 boards may overclock a bit better than B650 boards). X670 boards will be available alongside the first Ryzen 7000 CPUs in September, while B650 boards should follow in October.
Finally, in response to a question about cheaper and lower-end Zen 4 processors, AMD CEO Lisa Su told us that the AM4 platform isn't going anywhere in the near term.
"We do expect AM4 and AM5 to coexist for quite some time," said Su. "You should expect that, like with AM4, we'll build out the entire AM5 stack. But it will take some time to build out, and we want to make sure the cost points are right."
We'll provide more details on Ryzen 7000 CPUs, their integrated GPUs, and the AM5 platform ahead of a full review in late September.
Technology - Latest - Google News
August 30, 2022 at 06:30AM
https://ift.tt/iS2ao3w
AMD makes Ryzen 7000 official: Launching September 27, starting at $299 - Ars Technica
Technology - Latest - Google News
https://ift.tt/0CpnfVm
https://ift.tt/kXI18SN


0 Commentaires